
Want to hear from us?
Sign up to receive our latest email news, offers and updates.
Pet Food Industry News
July 18, 2022Do you know what vitamins your pet needs?
The word vitamin is derived from the word vital amine, which is essential to life. Thiamine was the first vitamin to be named. By extension, other substances with similar effects are also called vitamins.
Vitamins are divided into two families: fat-soluble vitamins (vitamins A, D, E, K: Table 1) and water-soluble vitamins (vitamin B: table 2). Fat-soluble vitamins accumulate in the body if overeating Cause poisoning, while water-soluble vitamins can be excreted through urine.
Many foods provide vitamins, and they can also be added to pet food in the form of premixes. Since they are sensitive to light, heat and oxidation, care should be taken when cooking and determining the shelf life of a product.
Each vitamin has a variety of different functions.
Vitamin A (Retinol)
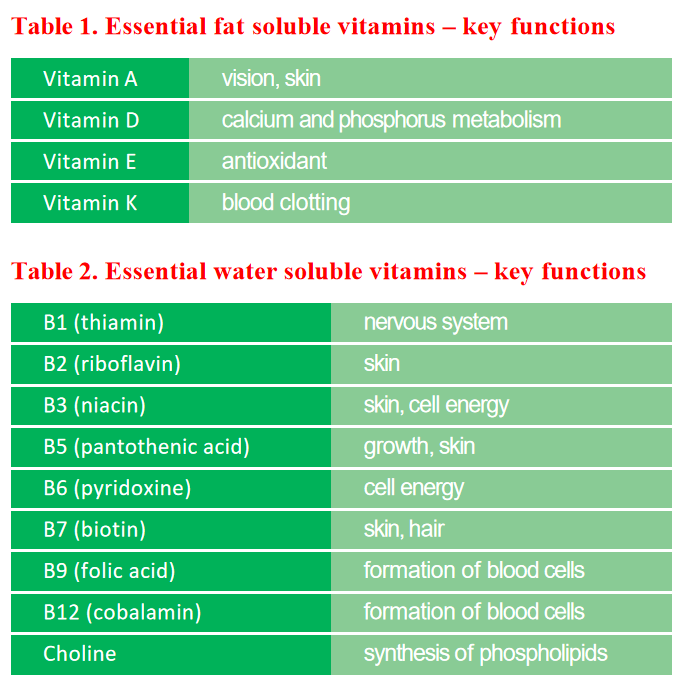
Vital for vision
Background
Vitamin A was isolated in 1913 and its chemical structure was drawn in 1931. It is a long chain alcohol that is soluble in fat. Absorbed in the small intestine and stored in the liver. Dogs can synthesize vitamin A from carotene, but cats lack the enzymes needed for this process. Both cats and dogs can digest large amounts of vitamin A.
Role in the body
Vitamin A is necessary for healthy vision, especially in dark environments. It is also involved in the synthesis of reproductive hormones and proteins, as well as in regulating skin cell growth and sebum production.
common sources
Good sources of dietary vitamin A are liver, fish and eggs.
Deficiency and Excess
A lack of vitamin A can lead to eye problems, dry skin, reproductive abnormalities, and increased sensitivity to infections and lung complications.
High levels of vitamin A can cause joint abnormalities and poor reproductive performance.
Vitamin D (cholecalciferol)
bone growth and calcification
Background
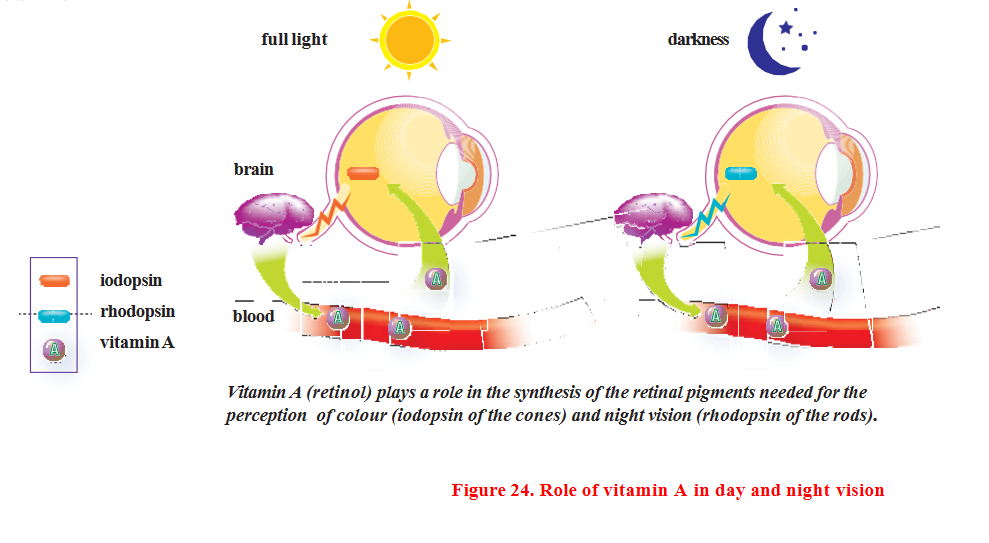
The benefits of cod liver oil for preventing rickets were discovered in 1782, and vitamin D was isolated in 1932. Humans and herbivores synthesize this vitamin in sunlight through skin sterols. However, this process is absent in cats and dogs, which means vitamin D must be provided in the diet. To remain active in the body, ingested vitamin D must be modified in the liver and kidneys.
Role in the body
Vitamin D plays a crucial role in the regulation of calcium and phosphorus metabolism by increasing intestinal absorption of these two minerals, optimizing calcium binding to bone, and reducing calcium and phosphorus loss in the urine.
Common sources
Meat and vegetables are almost completely deficient in vitamin D. Good sources of vitamin D include oily fish (sardines, tuna) and liver.
Deficiency and Excess
Vitamin D deficiency can lead to rickets (rare in dogs and cats), weight loss, and osteomalacia (joint and muscle pain, fractures).
Excessive intake of vitamin D can lead to reduced bone turnover and ossification in dogs, resulting in excessive bone calcification. In cats, excess vitamin D can cause soft tissue mineral deposition, hypercalcemia, depression, vomiting, and lethargy. This effect is most pronounced in puppies and kittens and can lead to bone abnormalities and soft tissue calcification.
Vitamin E (Tocopherol) Antioxidant - Protects the body from free radical damage
Background
Vitamin E was discovered in 1920 and isolated in 1936. Its antioxidant potential was not discovered until the 1980s. Vitamin E is a generic name for several substances. Alpha-tocopherol is the most common form and has the strongest biological activity. Vitamin E is stored in the fatty tissue of the liver and muscles. Diets high in polyunsaturated fatty acids require more vitamin E to prevent fatty liver disease.
Role in the body
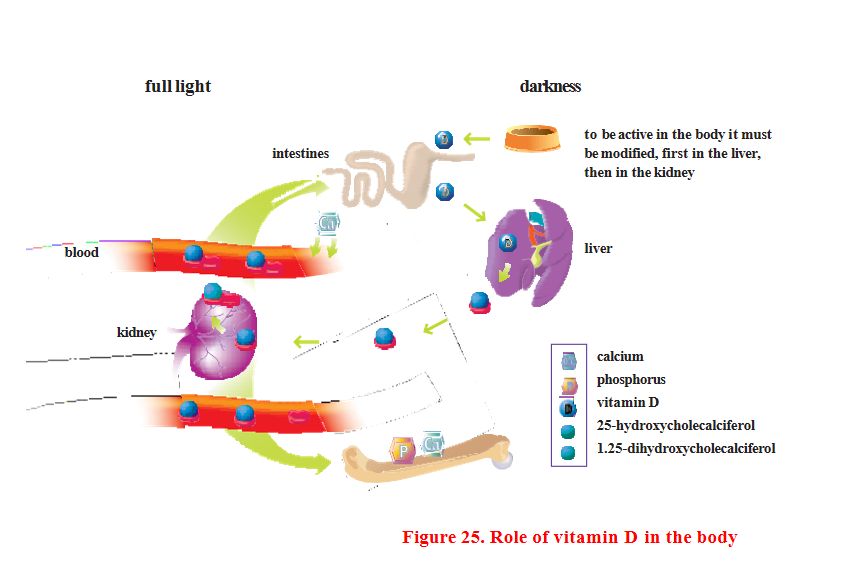
Vitamin E helps protect cells from free radicals. Cells generate free radicals through normal metabolism, thereby promoting the aging process. External factors that affect the body, such as exercise, pollution, and sunlight, also generate free radicals. Free radicals can cause cell death.
Vitamin E helps protect cell membranes from free radical damage and strengthens the immune system.
Common sources
The most important source of vitamin E is vegetables, followed by oils, grains and cereals. Vitamin E is also found in some animal products, such as liver.
Deficiency and Excess
Symptoms of deficiency in dogs and cats include muscle weakness, reproductive failure, retinal degeneration, and discoloration of fatty tissue.
Excessive vitamin E in cats has been shown to prolong blood clotting time. Vitamin E is the least toxic fat-soluble vitamin.
Vitamin K (MK-7 Menaquinone-7)
essential for blood clotting
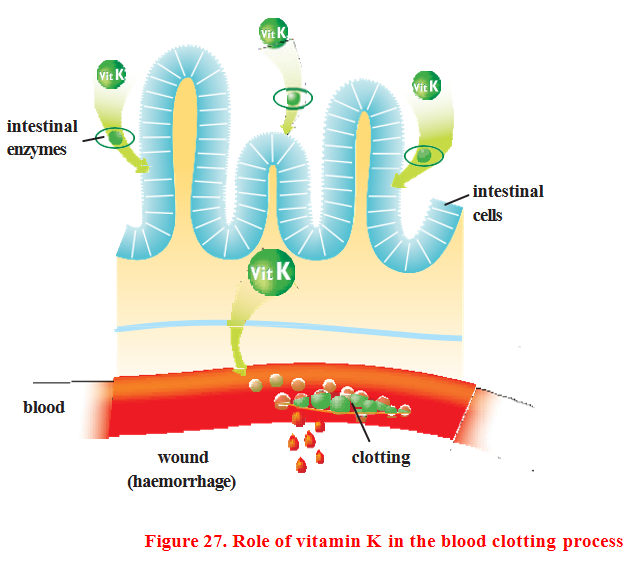
Background
In 1929 it was confirmed that dietary vitamin K prevents major bleeding, and in 1936 vitamin K was isolated. It is now known that vitamin K is one of a group of similar fat-soluble substances that can cause blood to clot through a complex biochemical pathway.
Role in the body
Vitamin K is a cofactor for many enzymes, which means that the enzyme must be active in the presence of vitamin K. Therefore, it is essential in certain blood clotting processes. It also plays a role in protein metabolism and the incorporation of calcium into bones. Vitamin K is normally stored in the liver.
Common sources
The gut bacteria of cats and dogs produce vitamin K. However, this process may not provide the full daily requirement of vitamin K, so a dietary supply is required. The main sources of vitamin K are liver, meat and vegetables such as spinach.
Deficiency and Excess
Vitamin K deficiency can cause bleeding in the digestive tract, nasal passages, skin, and brain due to insufficient blood clots.
Over time, these usually small bleeds can lead to anemia (a lack of red blood cells that carry oxygen in the blood).
Vitamin B1 (thiamine)
Essential for normal nerve function
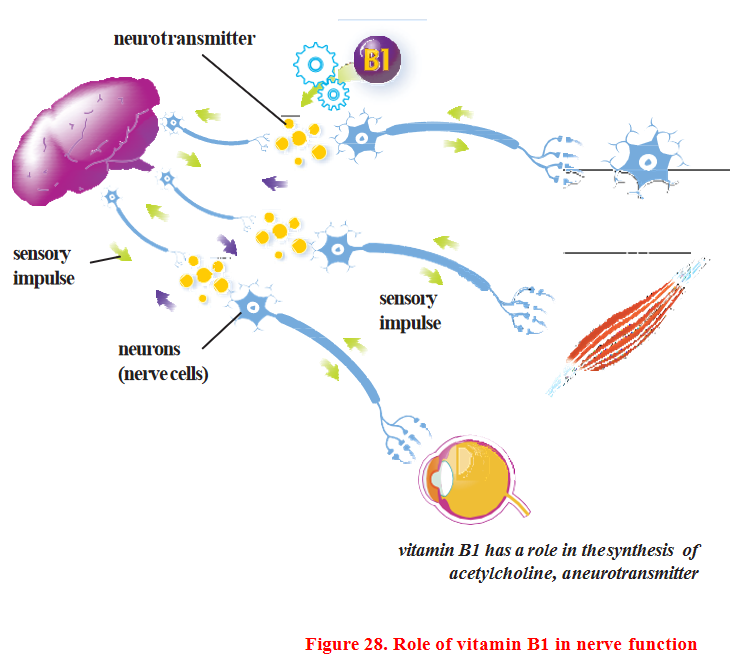
Background
Thiamine was the first vitamin to be discovered. Beriberi was observed in humans as early as 2600 BC, but its nutritional cause was not proven until 1885, and thiamine deficiency was identified as the cause of the disease in 1910. This vitamin dissolves in water and is concentrated in the heart, liver, kidneys and brain.
Role in the body
Thiamine is involved in many complex biochemical reactions that help cells produce energy. It is essential for the healthy functioning of the nervous system, helping to transmit sensory impulses.
Common sources
Yeast and wheat germ have the highest levels of thiamine, but it's also found in meat, bran, and grains
Deficiency and Excess
Thiamine deficiency can cause beriberi in humans, and animals experience fatigue, muscle weakness, gait and vision problems, seizures, and eventually death.
ctpet insists on continuous innovation, provides customers with OEM&ODM pet snacks, and pays attention to the health and nutritional balance of pets.
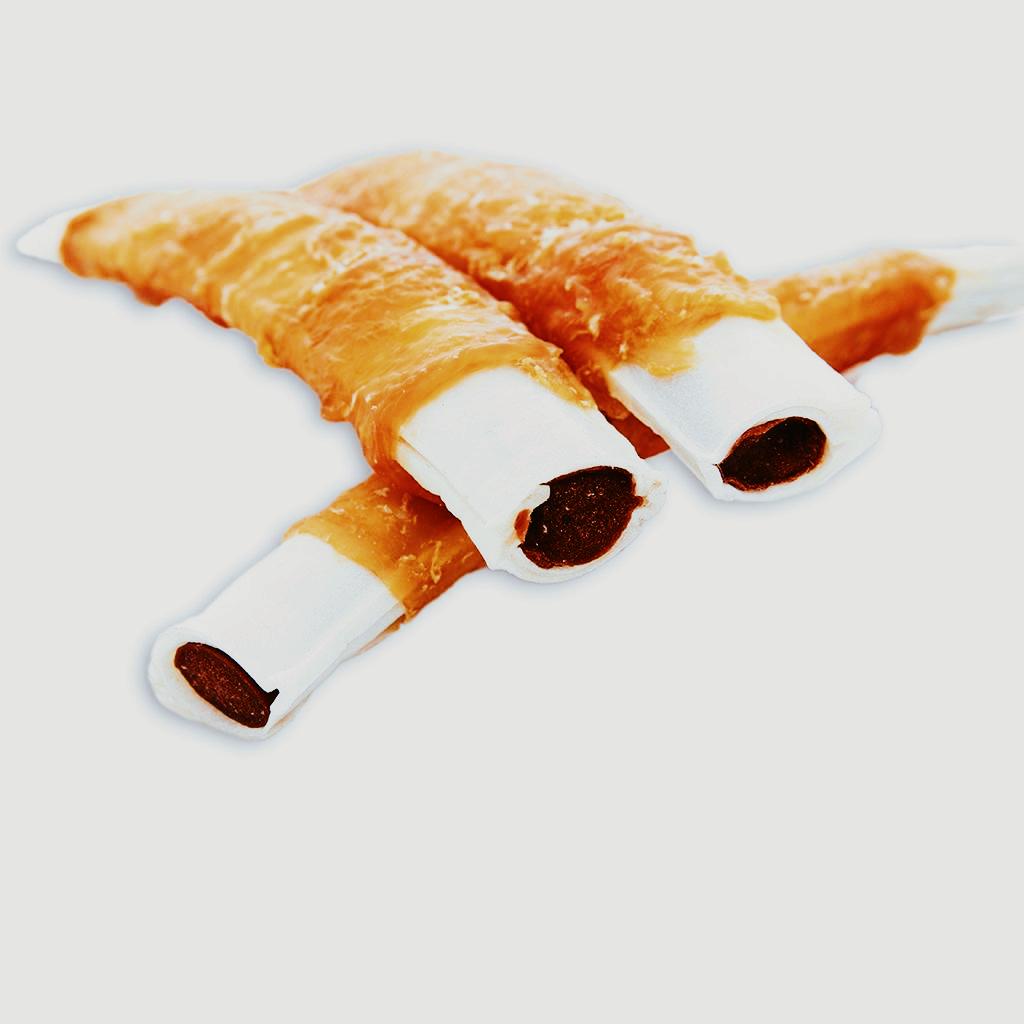
Liver Filled Ribed with Chicken
The full chicken enhances the palatability, and the dogs can't help drooling.
The ribs are 100% pure rawhide, which enhances the toughness and allows the dog to enjoy it for a longer time.
The liver filled inside can be customized to taste, and the exclusive formula is nutritionally balanced to meet different preferences and triple the taste.

If you wanna get more knowledge about dog treats, cat treats, dog dental snacks, rawhide dog treats, non-hide dog treats, rawhide free dog dental snacks, welcome to visit ctpet pet treats website: www.ctpetfood.com, www.ctpetfood.cn, www.chaotaipet.com
Welcome to contact Caroline Lee: caroline@chaotaipet.com

Want to hear from us?
Sign up to receive our latest email news, offers and updates.
